Car insurance costs have been on the rise for years, and with the imposition of new tariffs on automobile parts and materials, the trend is set to continue. Tariffs—essentially taxes imposed on imported goods—can have a significant impact on the automotive industry, increasing the price of vehicles and repair costs. As a result, insurance companies are forced to adjust their premiums to account for higher claims payouts. This article delves into the reasons why tariffs contribute to the rising cost of car insurance and what consumers can expect in the future.
Insurance Rates Continue to Rise
Auto insurance rates have been on a steady upward trajectory since 2022, and new projections suggest that costs will increase another 5% in 2025. According to industry reports, auto insurance rates soared 15% in 2024, while EV insurance costs for nine popular models jumped 28% over the same period.
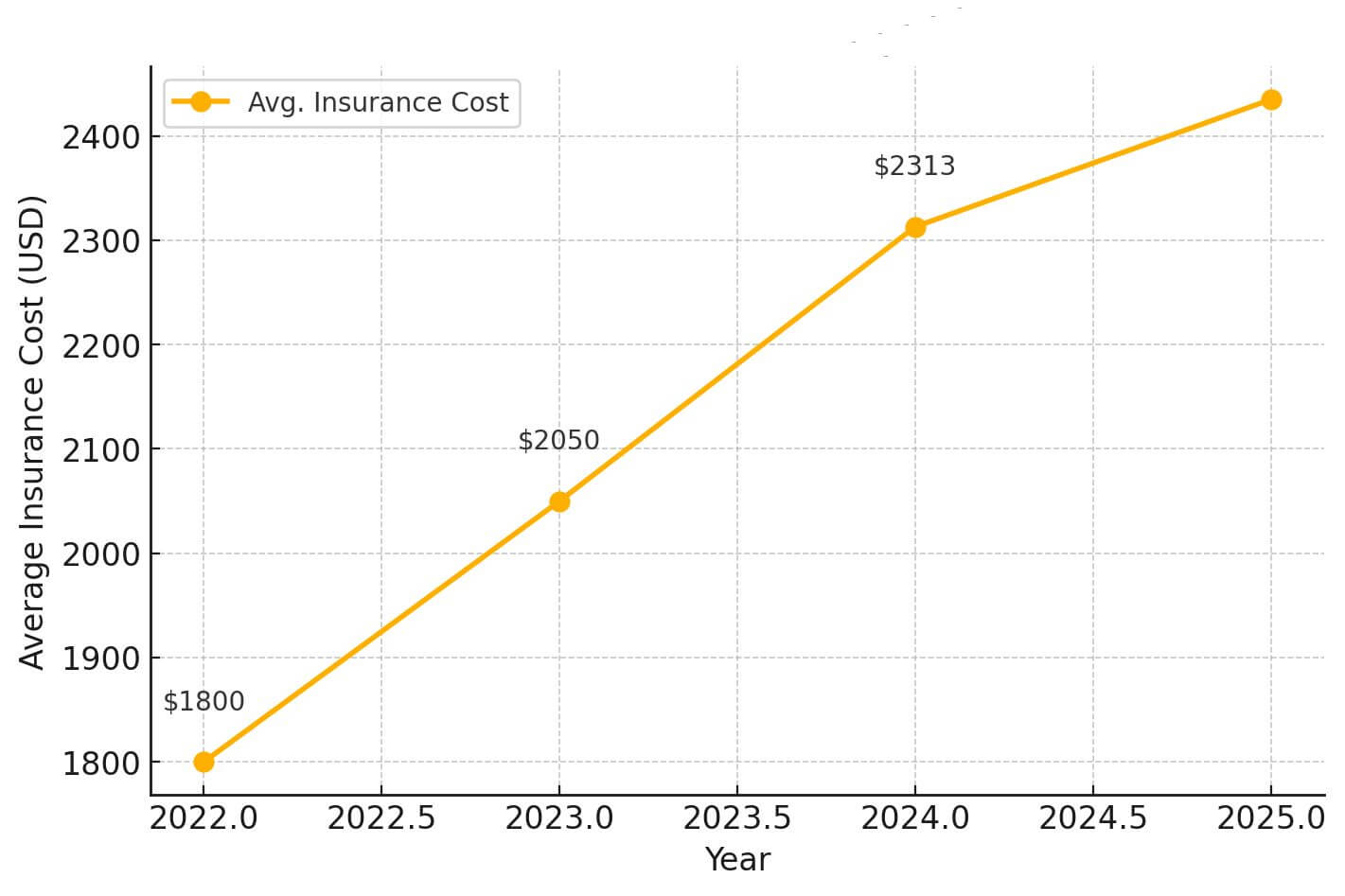
Today, the average cost of full-coverage auto insurance is $2,313 per year, but for many drivers, it’s far worse. In six states, annual premiums exceed $3,000, making car ownership even more expensive. Many drivers fail to plan for insurance costs prior to purchasing a vehicle, making insurance expenses one of the hidden costs of vehicle ownership, alongside depreciation.
Why Are Auto Insurance Rates Rising in 2025?
Several factors are driving the increase in car insurance costs, including:
- Rising Vehicle Repair Costs: As cars become more technologically advanced, repairs are more expensive. This is especially true for EVs, which tend to have higher repair costs than gas-powered vehicles. Even ICE vehicles have costly electronic components these days, making it more difficult to avoid the risks of costly repairs.
- Climate Risk Adjustments: Insurers are increasingly factoring climate risks into their rates. More frequent hurricanes, wildfires, and severe weather events are leading to higher claims payouts, which results in rising premiums for all drivers.
- Previous Insurance Industry Losses: In 2022, insurers faced a record $33.1 billion in underwriting losses, prompting a 24% increase in full-coverage policy costs in 2023. While the market is stabilizing, insurers are still adjusting their pricing models.
Some states are seeing a bit of relief. In the second half of 2024, average premiums decreased in 21 states. However, projections indicate that drivers in Florida, New York, Georgia, Nevada, and Delaware will see the biggest rate hikes in 2025, with full-coverage rates expected to rise another 10% in these high-cost states. Nationwide, the average auto insurance premium is forecast to reach $2,435 in 2025.
How Trump’s Proposed Tariffs Could Affect Auto Insurance
Many of us haven’t had to ponder the nuance of tariffs since 9th-grade history class. That is until this election season when President Trump proposed a 10 to 20 percent tariff on all goods imported into America. The president has since suggested various tariff amounts, from a 60 percent tariff on products from China to a 200 percent tax on John Deere imports (yes, the tractor company).
However, on November 25, 2024, Trump stated his plan loud and clear in a post on Truth Social. His plans include an inauguration day executive order to implement a 25 percent tariff on all products coming into the country, plus an additional 10 percent tariff on Chinese products.
With Mexico and Canada being two of America’s major suppliers of imported cars, these tariffs can directly impact the cost of purchasing, maintaining, and insuring a vehicle for most drivers. These tariffs could impact auto insurance costs in a few ways:
- More expensive vehicles and repairs: If auto insurance companies are paying out more to repair and replace vehicles after covered claims, they will pass these costs along to consumers in the form of higher premiums.
- Shipping delays: Companies look for new suppliers to circumvent tariffs, which can disrupt global trade flows and cause shipping delays, increasing costs.
- Delays in repairs: Shortages in vehicle parts, like those seen during COVID-19, could extend repair times, leading to increased rental car costs.
- Increase in totaled vehicles: Higher repair costs could lead to more vehicles being deemed total losses, forcing consumers to buy new cars sooner than anticipated.
How Tariffs Affect Car Insurance Premiums
Car insurance premiums are determined based on several factors, including the cost of repairing or replacing vehicles. As tariffs drive up auto-related expenses, insurance rates follow suit for several reasons:
- Higher Repair Costs Lead to Higher Claims Payouts
When car parts become more expensive due to tariffs, repairing a damaged vehicle costs insurers more money. Since insurance companies must cover these repairs through claims payouts, they compensate by raising premiums across the board.
- Increased Car Prices Mean Higher Replacement Costs
If a car is deemed a total loss after an accident, insurers must pay out the replacement value. With tariffs inflating vehicle prices, the cost of replacing a car becomes more expensive, leading to higher insurance costs.
- Rise in Auto Theft Claims Due to Expensive Parts
As vehicle parts become costlier, stolen cars and auto parts become more lucrative for criminals. This can lead to a rise in auto theft claims, further increasing insurance costs for all drivers.
- Supply Chain Delays and Increased Repair Times
Tariffs can disrupt global supply chains, causing shortages of crucial car parts. This can lead to longer repair times, forcing insurance companies to pay for extended rental car coverage, adding another layer of costs that gets transferred to policyholders.
Consumer Impact: What Can Drivers Do?
With rising car insurance costs due to tariffs, drivers should consider the following strategies to manage their expenses:
- Shop Around for the Best Rates: Comparing multiple insurance providers can help secure a competitive premium.
- Opt for Higher Deductibles: Choosing a higher deductible can lower monthly premiums, though it requires paying more out-of-pocket in case of a claim.
- Take Advantage of Discounts: Many insurers offer discounts for safe driving, bundling policies, or installing anti-theft devices.
- Drive a Vehicle with Lower Repair Costs: Some vehicles are more expensive to repair than others. Researching insurance costs before purchasing a car can help save money in the long run.
Conclusion
Tariffs on auto parts and materials directly contribute to increased car insurance premiums by raising repair and replacement costs. As insurers adjust their rates to accommodate these higher expenses, drivers bear the financial burden. While tariffs may be aimed at supporting domestic industries, they often create ripple effects that impact everyday consumers. To mitigate these rising costs, drivers should explore different insurance options, look for discounts, and make informed choices when purchasing a vehicle.